안드로이드 DB(데이터베이스)를 사용하는 방법을 알아 보겠슴다.
데이터베이스를 이용하는 곳이 많은 만큼 중요한 것이고, 가독성을 높이기 위해서 여러 글로 나누어서 작성하려고 합니다.
우선은 안드로이드 DB(데이터베이스) 1편 'DB 생성'입니다.
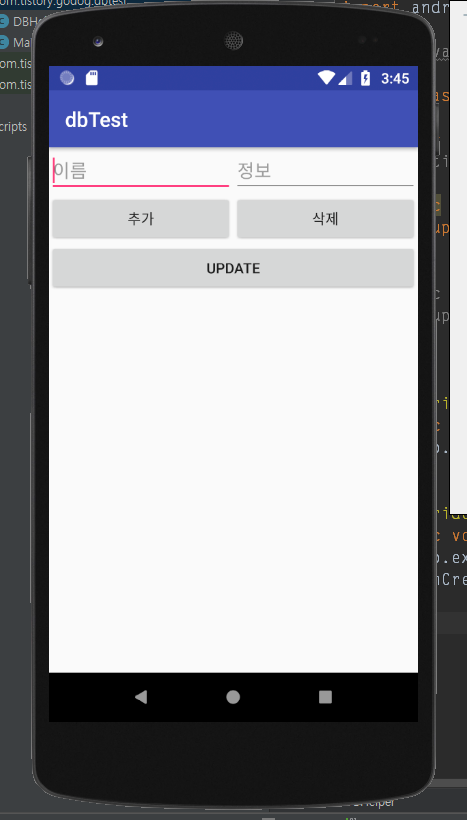
실행 화면

/* 메인 레이아웃(activity_main.xml) */

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="이름"
android:inputType="textPersonName" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="정보"
android:inputType="textPersonName" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:onClick="insert"
android:text="추가" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:onClick="delete"
android:text="삭제" />
</LinearLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="listUpdate"
android:text="Update" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
</ListView>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
주 내용은 데이터베이스이므로 대충 그냥 리스트뷰를 2개 사용하여서 각각 출력하도록 만들었다.
하지만 데이터베이스를 사용할 때 보통 같이 쓰는 것 중 하나가 바로 커스텀 리스트 뷰인데 이에 관하여서는
해당 글을 참조하여서 만들어보는 것을 추천한다.
/* 메인 자바 코드 ( MainActivity.java ) */
package com.tistory.godog.dbtest;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
EditText editText, editText2;
ListView listView, listView2;
DBHelper dbHelper;
SQLiteDatabase db = null;
Cursor cursor;
ArrayAdapter adapter, adapter2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
editText = findViewById(R.id.editText);
editText2 = findViewById(R.id.editText2);
listView = findViewById(R.id.listView);
listView2 = findViewById(R.id.listView2);
dbHelper = new DBHelper(this, 3);
db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase(); // 읽기/쓰기 모드로 데이터베이스를 오픈
}
}
- 우선은 데이터베이스 생성만을 알아보는 것이므로 메인에서는 변수 선언과 초기화 말고 별거 없다.
- 18라인 : 만들어야 할 클래스 파일.
- 19라인 : SQLiteDatabase에는 SQL 명령을 생성, 삭제, 실행하고 기타 일반적인 데이터베이스 관리 작업을 수행하는 메소들이 있다.
- 20라인 : Cursor는 안드로이드에서 DB에서 가져온 데이터를 쉽게 처리하기 위해서 제공하는 2차원 테이블을 가지는 인터페이스이다.
이제 18라인에서 만들어야 한다고 했던 자바 파일을 만들기 위해서 자바 파일만을 하나 생성해준다.

/* DBHelper.java */
package com.tistory.godog.dbtest;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
static final String DATABASE_NAME = "test.db";
//static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 2;
public DBHelper(Context context, int version) {
super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, version);
}
/*
public DBHelper(Context context, String name, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int version) {
super(context, name, factory, version);
}
*/
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
db.execSQL("CREATE TABLE tableName ( name TEXT, info TEXT);");
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
db.execSQL("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS tableName");
onCreate(db);
}
}
- 파일을 생성하였으면 SQLiteOpenHelper를 상속받아준다.
- SQLiteOpenHelper는 데이터베이스 생성 및 버전 관리를 관리하도록 도와주는 클래스이다.
+ 상속을 받아준 후 클래스 안에서 "Ctrl+i"를 눌러서 모두 추가해 준 후,
"Alt + Insert"->"Constructor"로 생성자 하나를 추가해주면 기본적인 세팅은 끝난다.
- 주석된 부분을 보면 본래 생성자를 볼 수 있다. 이는 선언한 생성자와 많이 매개변수가 다른데 별 의미는 없다. 단, 데이터베이스 파일을 하나만 사용할 경우 위처럼 상수로 데이터베이스 이름과 버전을 선언해두고 인수로 줌으로써 에러를 줄이고 수정을 용이하게 만든다.
(+ 보통 파일 내에서 테이블 단위로 나눌 수 있으므로 db파일을 하나만 사용한다. )
- onCreate : 데이터베이스가 처음 생성될 때 호출된다. 그러므로 테이블의 생성이 일어난다.
※ execSQL : Select 명령 외에 SQL 명령들을 실행한다.
- 23라인 : 괄호 안을 보면 ( name TEXT, info TEXT)로 되어있다. 이는 ( '열 항목명' '데이터 형', )이다. 숫자 데이터 형을 만들려면 "(num INTEGER)" 이렇게 만들면 된다.
- onUpgrade
여기까지 데이터베이스 생성 및 관리를 도와주는 SQLiteOpenHelper를 상속받은 클래스 파일을 만들었으면 데이터베이스를 만들 준비는 끝났다.
다음 글에서는 이어서 데이터베이스의 데이터를 추가, 삭제하는 방법을 알아보겠다.